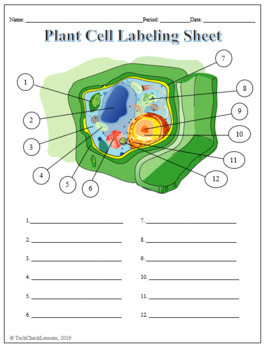
44 plant cell labels and functions
Plant Cell - Definition, Diagram, Parts, Function, Structure & Types Functions of a Plant Cell Photosynthesis is the major function performed by plant cells, and therefore these are known as the building blocks of plants. Photosynthesis is the process that occurs in the chloroplasts of the plant cell. It is the process by which plants prepare their food utilizing sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide. Plant Cell - Definition, Structure, Function, Diagram & Types - BYJUS Plant Cell Functions Plant cells are the building blocks of plants. Photosynthesis is the major function performed by plant cells. Photosynthesis occurs in the chloroplasts of the plant cell. It is the process of preparing food by the plants, by utilising sunlight, carbon dioxide and water. Energy is produced in the form of ATP in the process.
What is Plant cell? Introduction, Structure, and Functions, with ... Introduction -. Plants are multicellular organisms and their cells are eukaryotic. Like animal cells, the plant cells have membrane bound organelles and a nucleus. However, the plant cell differs from animal cells in many aspects. The plant cells have some special organelles that allows the cells to carry out photosynthesis.

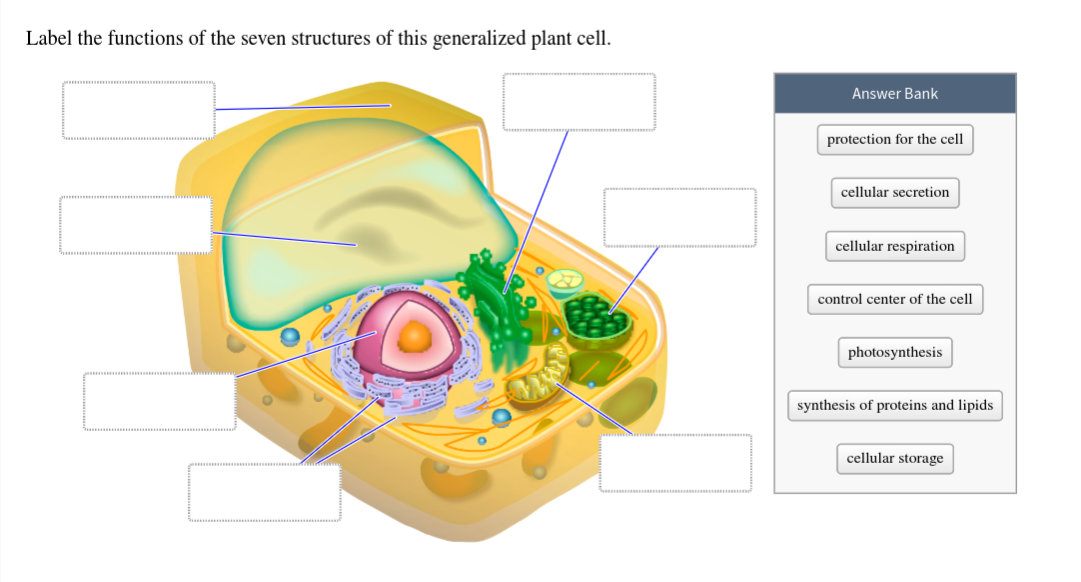
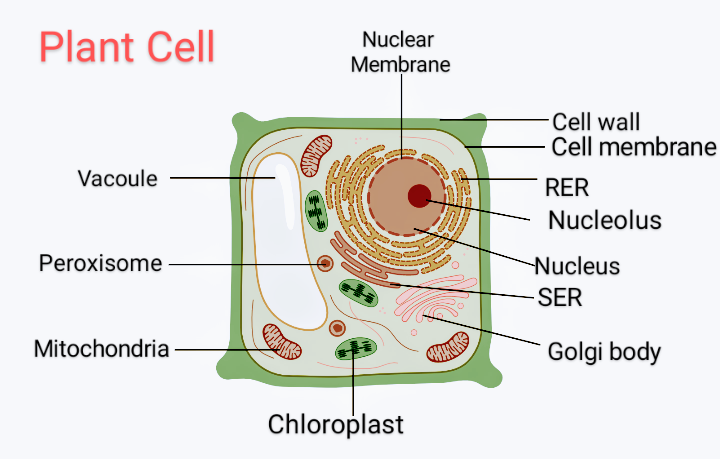
Plant cell labels and functions
Labeled Plant Cell With Diagrams | Science Trends The cell wall's function is to give protection to the cell and to support it. The cell wall must be both permeable yet rigid. It must be permeable so that materials can move in and out of the cell, but rigid enough that it supports and protects the cell. Cell walls are composed out of carbohydrate polymers referred to as cellulose. Plant Cell Structure and Parts Explained With a Labeled Diagram Plant cells are classified into three types, based on the structure and function, viz. parenchyma, collenchyma and sclerenchyma. The parenchyma cells are living, thin-walled and undergo repeated cell division for growth of the plant. They are mostly present in the leaf epidermis, stem pith, root and fruit pulp. Plant Cell- Definition, Structure, Parts, Functions, Labeled Diagram The function of the plant cell wall. The primary role of the cell wall is defined to be a mechanical and structural function, that is highly effective in serving the plant cell. These functions include: Providing the cell with mechanical protection and shielding the cell from the chemically harsh environment, provided by the secondary wall layer.
Plant cell labels and functions. A Labeled Diagram of the Plant Cell and Functions of its Organelles ... Its functions include, isolating materials harmful to the cell, maintaining turgor within the cell and exporting unwanted materials away from the cell. Function: Regulates internal environment. You can save and print this diagram of the plant cell. It will help you with your revision. That's about how the organelles in a cell function. Plant Cell Labeling and functions Flashcards | Quizlet Finishes, stores, distributes protein products of the cell. Function of Cytoplasm An inner layer of the prokaryotic cells that is rich is protein with gel-like consistency; it houses organelles. in eukaryotic cells, it contains the cell contents and the organelles and is gel-like. Recommended textbook solutions Biology Plant Cell Parts | Their Structure and Functions - Study Read Its functions include. To protect the entire cell from harsh environmental conditions. To prevent drying of the cell by loss of water. Allow the passage of a few substances like water into and out of the cell. 2. Cell membrane. This is also called a plasma membrane and is present adjacent to the cell wall. Types of Plant Cell- Definition, Structure, Functions, Labeled Diagram The plant cell has a well-defined cell wall made up of cellulose components, plastids that perform photosynthesis and storage of carbohydrates in form of starch, central vacuoles for regulating the cell's turgor pressure, and a nucleus which controls the cells' general mechanisms including reproduction of the plant cells.
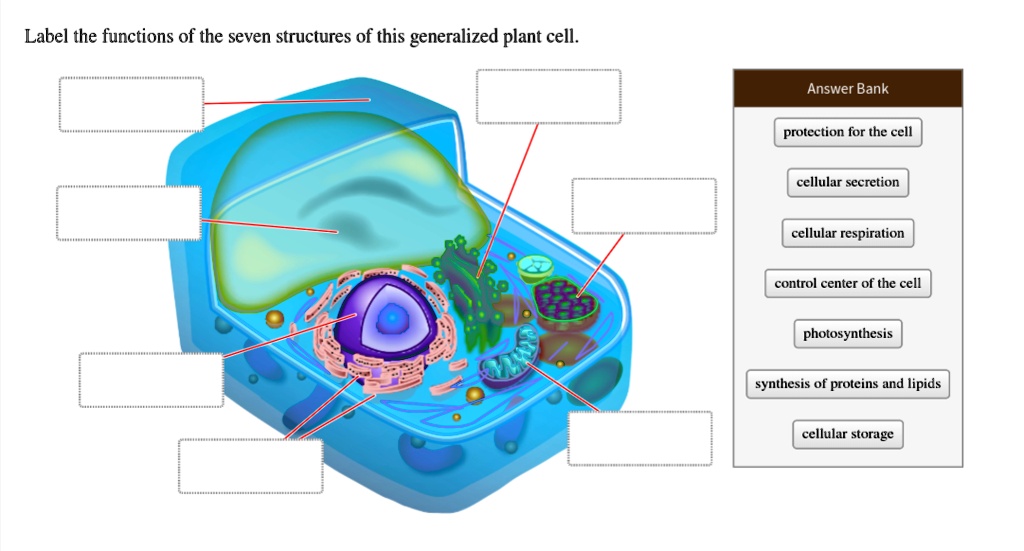
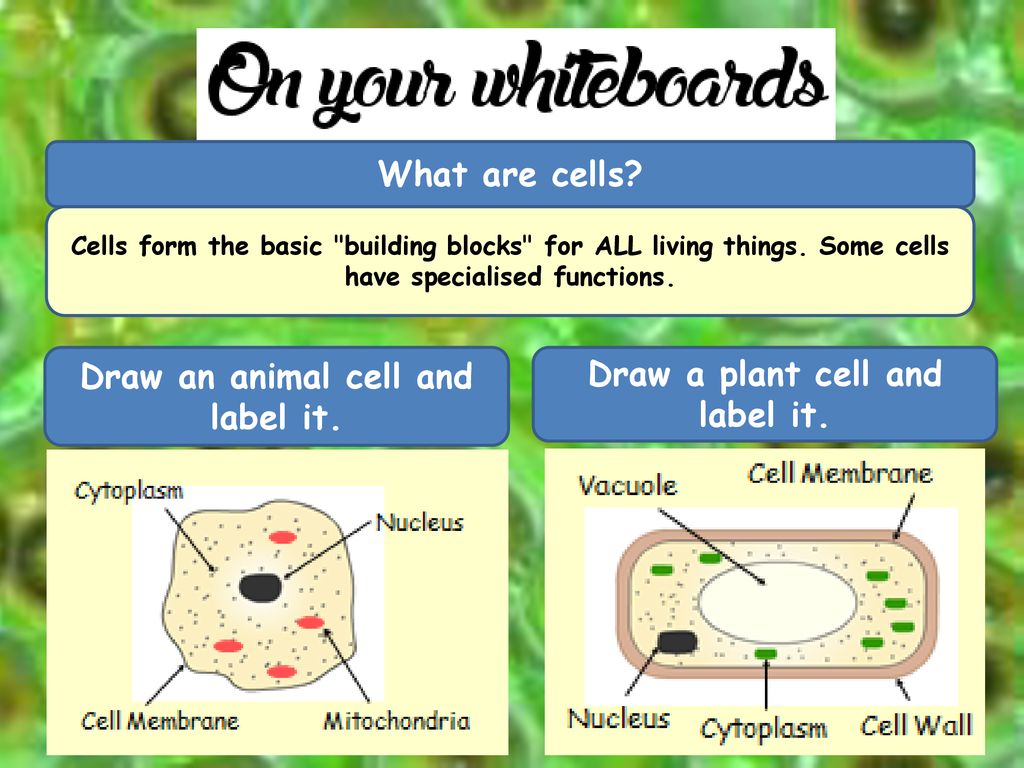
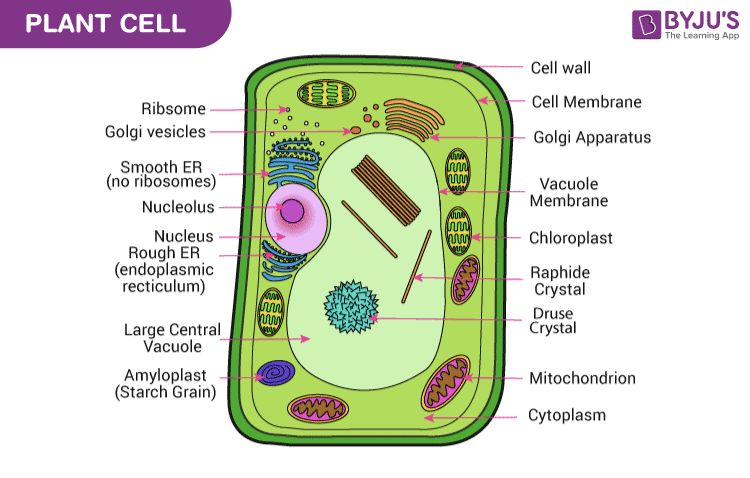
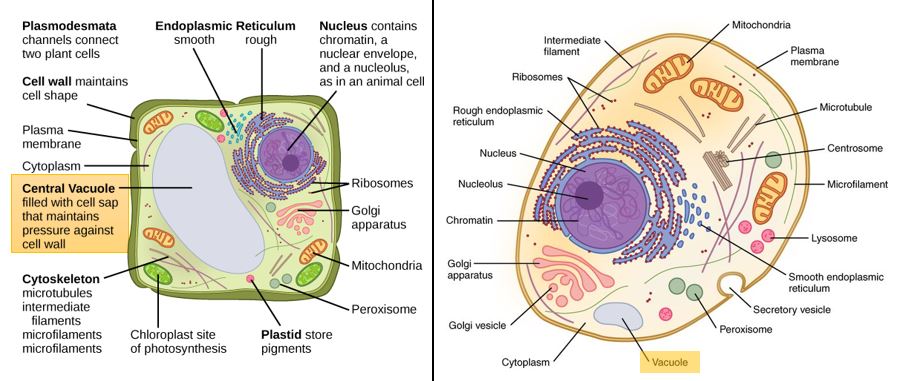
Organelles of the plant cell and their functions - Learner trip 1. INTRODUCTION. The plant cell has 18 different types of organelles ¹ with specialized functions.. Below you can find a list will all of them (plant cell organelles and their functions) with and image/diagram to help you visualize where they are and how they look within the cell.. 2. ORGANELLES OF THE PLANT CELL AND THEIR FUNCTION. Plasma membrane: Separates the cell from its environment ... Label Cell Parts | Plant & Animal Cell Activity | StoryboardThat Click "Start Assignment". Find diagrams of a plant and an animal cell in the Science tab. Using arrows and Textables, label each part of the cell and describe its function. Color the text boxes to group them into organelles found in only animal cells, organelles found in only plant cells, and organelles found in both cell types. Plant Cell-Definition, Structure, Parts, Functions, Labeled Diagram Organelles are responsible for a range of functions, including the production of hormones and enzymes and the delivery of energy to plant cells. Plant cells include DNA that aids in the formation of new cells, allowing the plant to grow faster. The nucleus, an encapsulated membrane structure in the cell's core, contains the DNA. Plant Cell Structures and Functions | Let's Talk Science This is a very important function in plants. Plant cells contain vacuoles. Most adult plant cells have one large vacuole that takes up more than 30% of the cell's volume. At certain times and conditions the vacuole takes up as much as 80% of the cell's volume! In addition to storing wastes and water, the vacuole also helps to support the cell.
Plant cells - Cell structure - AQA - GCSE Combined Science ... - BBC Plant cells This basic structure of a plant cell is shown below - the same plant cell, as viewed with the light microscope, and with the transmission electron microscope. Animal and... The Label Plant Cell: A Better Way to Understand 13 Plant Structure and ... The Label Plant Cell is a method that uses tiny, colored dots to label individual cells in a plant. With this method, scientists can track the movements and interactions of individual cells in a plant, which can help them better understand how plants function. The Label Plant Cell is a new way to study plant structure and function. Free Printable Plant and Animal Cells Worksheets - Homeschool Giveaways Worksheets to Label Plant and Animal Cells. Plant and Animal Cell Worksheets and Printables - These plant and animal cell worksheet diagrams are scientifically accurate, so are a great way to help young scientists get a clear idea of what a cell looks like. Plant Cell and Animal Cell Diagram Labeling Quiz - After your plant cell and animal ... Plant Cells: Labelled Diagram, Definitions, and Structure - Research Tweet Plastids and Chloroplasts. Plants make their own food through photosynthesis. Plant cells have plastids, which animal cells don't. Plastids are organelles used to make and store needed compounds. Chloroplasts are the most important of plastids. They convert light energy from the sun into sugar and oxygen. The most exposed parts of the plants ...
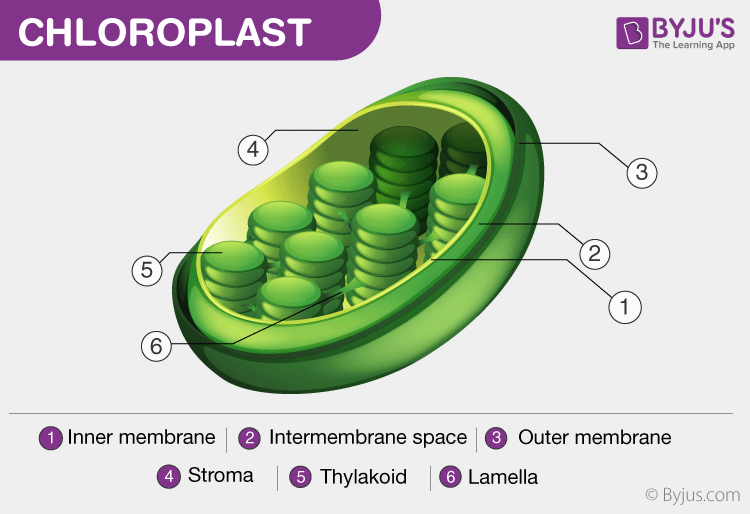
Plant Cell Parts And Functions | Science Trends The chloroplast is one of the most important parts of the plant cell and is crucial to its function. As is commonly known, plants use photosynthesis to harness the power of the sun to create nutrients. The sunlight is used to turn carbon dioxide and water into sugar and oxygen, a waste product.
Plant Cell Labeling | Plant Game | Turtle Diary Identify and label figures in Turtle Diary's fun online game, Plant Cell Labeling! Drag the given words to the correct blanks to complete the labeling!
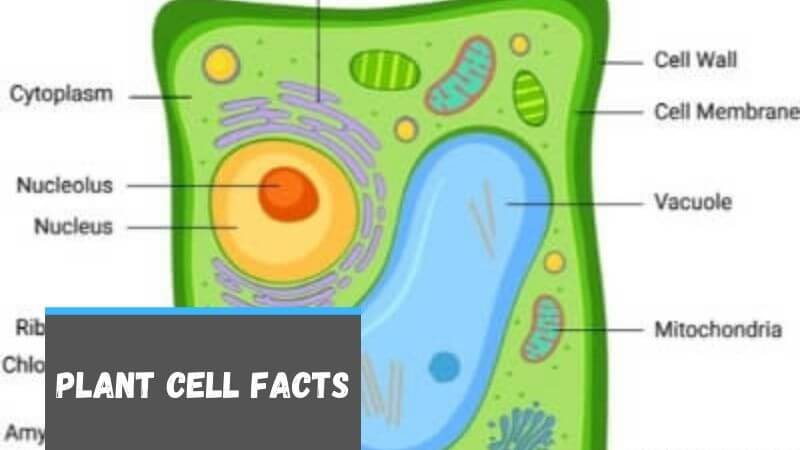
Plant Cell Facts for Kids (Explained!) - Education site Fun Plant Cell Facts. Plant cells are unique - Plant cells are the only known things on earth that can produce their own food by themselves. Animals and plants are interdependent - The process of photosynthesis leaves oxygen that plants give off into the atmosphere. Animals and most of earth's life depend on that oxygen to live.
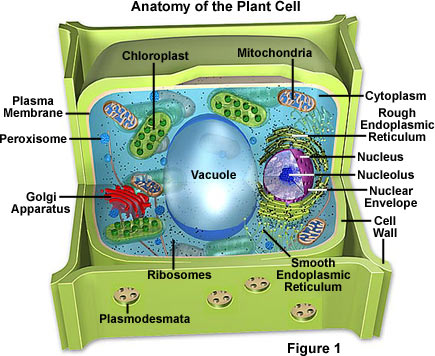
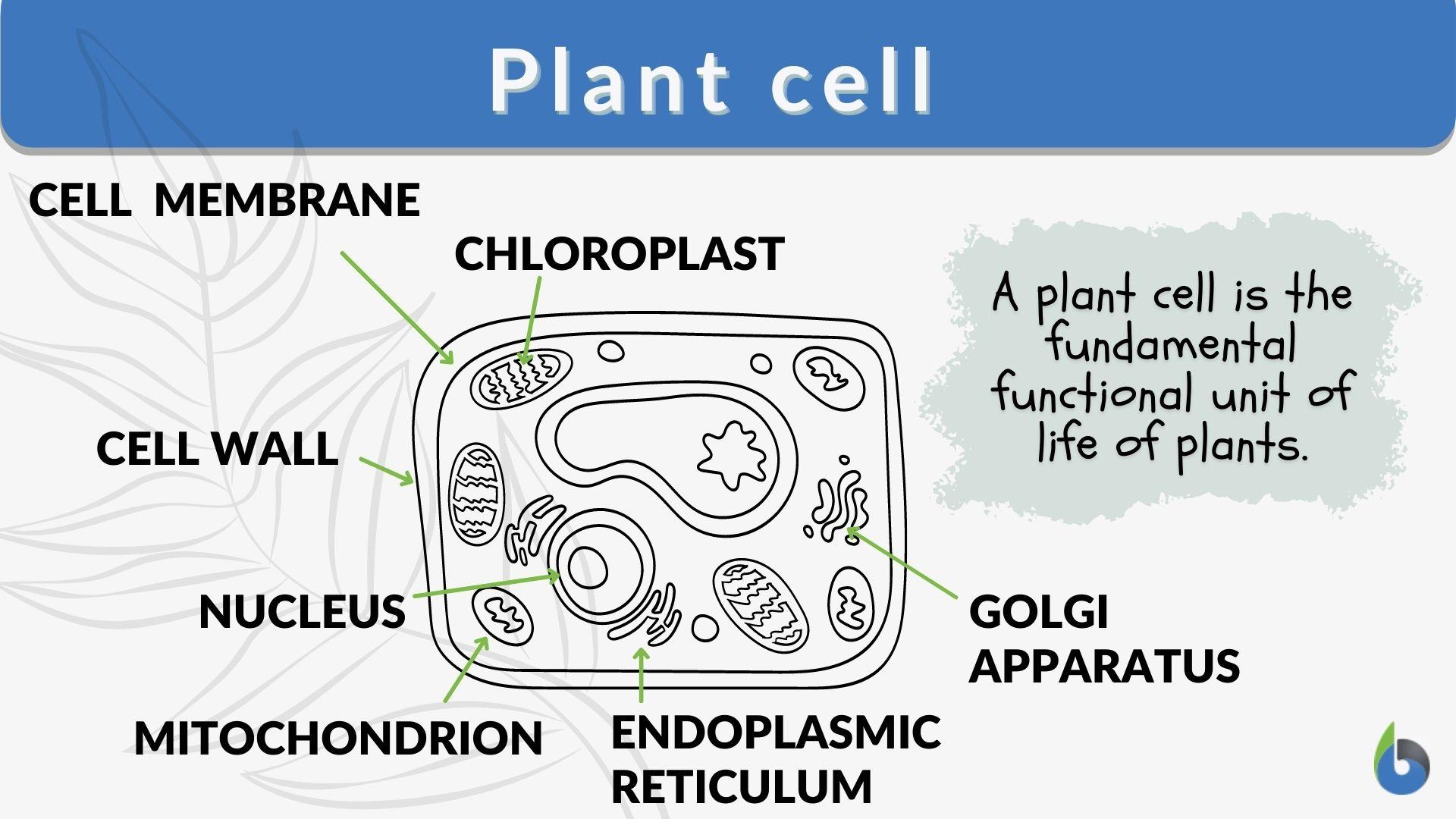
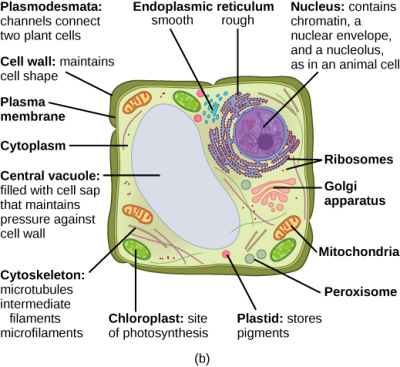
Plant Cell Organelles: Functions & Structures | StudySmarter Plants have all the typical features of eukaryotic cells: plasma membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, ribosomes, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, vesicles, and cytoskeleton. Exclusive organelles and structures of plant cells compared to animal cells are vacuoles (including a large central vacuole), plastids, and cell walls.
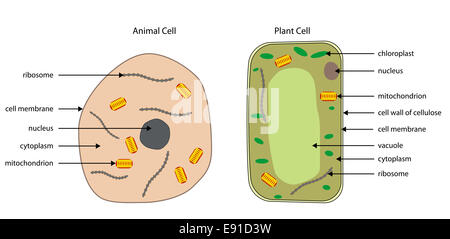
Plant and Animal Cells: Definition, Structure, and Function- Embibe Plant Cell: Plant cells are eukaryotic cells with a true nucleus along with specialized structures called organelles that carry out certain specific functions. Animal Cell: An animal cell is a type of eukaryotic cell that lacks a cell wall and has a true, membrane-bound nucleus along with other cellular organelles. Diagram of Plant and Animal Cell
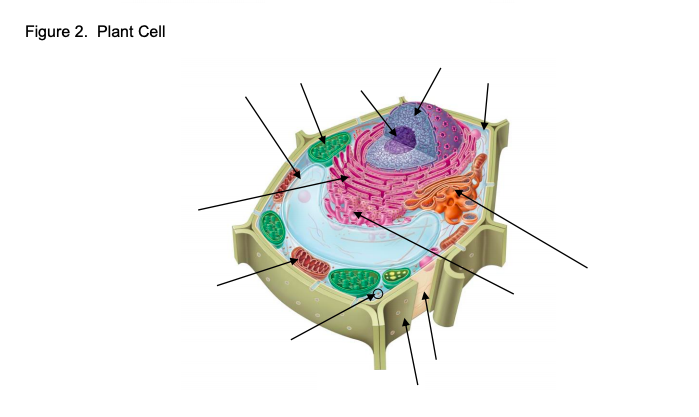
Plant Cell - The Definitive Guide | Biology Dictionary A diagram of a plant cell with the organelles labeled. The plant cell has many different features that allow it to carry out its functions. ... There are five types of tissue formed by plant cells, each with different functions. Parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma are all simple plant tissues, meaning they contain a single cell type. ...
Plant Cell Definition, Function, Facts And Structure | Biology Topics Cell Wall. As the name suggests, the cell wall is the outer covering of the plant cell. The primary function of the cell wall is to protect the inner components of the plant cell. But, this is not its only function. This component is also giving the plant cell its shape. In the plant cell, the constituents of the cell wall are mainly: Cellulose.
PDF Plant Cells - Definition, Diagram, Structure & Function - NFEI A plant cell is a eukaryotic cell that contains a true nucleus and certain organelles to perform specific functions. However, some of the organelles present in plant cells are different from other eukaryotic cells. What are the different types of plant cells? The different types of plant cells include- collenchyma, sclerenchyma, parenchyma, xylem and phloem.
Plant Cell: Definition, Types of Plant Cells and More - Embibe Plant Cell Wall. It is a rigid layer that is composed of cellulose, glycoproteins, lignin, pectin ...
Plant Cell Parts & Functions | What is a Plant Cell? - Study.com Plant Cell Function; Parenchyma: Participate in photosynthesis, food storage and removal of ...
Plant Cell Wall- Definition, Structure, Functions, Diagram Functions of plant cell wall It provides mechanical support as the skeletal framework in the plant. It protects the inner components of the cell from mechanical injuries. It is permeable to the water and solutes. It is the presence of the water-filled channels which allows the free diffusion of water and water-soluble substances.
Plant Cell- Definition, Structure, Parts, Functions, Labeled Diagram The function of the plant cell wall. The primary role of the cell wall is defined to be a mechanical and structural function, that is highly effective in serving the plant cell. These functions include: Providing the cell with mechanical protection and shielding the cell from the chemically harsh environment, provided by the secondary wall layer.
Plant Cell Structure and Parts Explained With a Labeled Diagram Plant cells are classified into three types, based on the structure and function, viz. parenchyma, collenchyma and sclerenchyma. The parenchyma cells are living, thin-walled and undergo repeated cell division for growth of the plant. They are mostly present in the leaf epidermis, stem pith, root and fruit pulp.
Labeled Plant Cell With Diagrams | Science Trends The cell wall's function is to give protection to the cell and to support it. The cell wall must be both permeable yet rigid. It must be permeable so that materials can move in and out of the cell, but rigid enough that it supports and protects the cell. Cell walls are composed out of carbohydrate polymers referred to as cellulose.










(136).jpg)









:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/animal-cells-vs-plant-cells-373375_final-5b462d7fc9e77c00375014f1.png)



Post a Comment for "44 plant cell labels and functions"